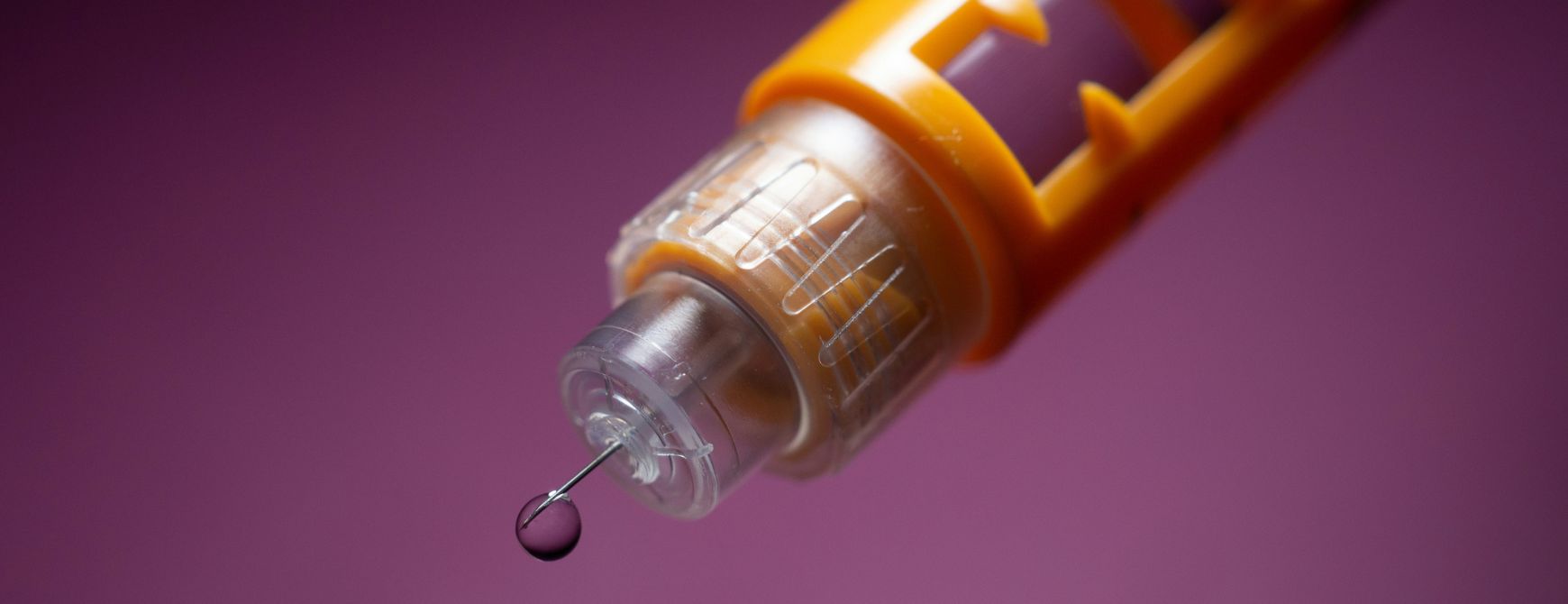
Diabetes affects more than 830 million people worldwide, yet access to insulin remains limited in many regions due to costly and fragile cold-chain requirements. The development of thermally stable, cold-chain-independent insulin represents an urgent solution that can significantly improve treatment accessibility while addressing broader stability challenges in biopharmaceuticals.
Areas
Health
Fields of use
Thermally-stable insulin for broader and easier diabetes treatment; biopharmaceutical (biologics) development
Intellectual property
International Patent Application No. PCT/EP2025/078804 (PCT application based on LU508453), »Polypeptides having NH-triazole functionalizations«.
Developed by
University of Ljubljana (Faculty of Chemistry and Chemical Technology, Faculty of Medicine) and Jožef Stefan Institute
Contact
Download PDF
- Termostable insulin_ENG.pdf (pdf, 242 KB)
Background
About 830 million people currently live with diabetes, projected to reach 1.3 billion by 2050. Insulin is essential but often inaccessible in low and middle income regions due to strict cold chain requirements. Because current insulin must be stored at ~4 °C, distribution is costly and prone to failures.
A heat stable, cold chain independent insulin would greatly expand access, reduce supply chain losses, and lower costs. The WHO has identified this need as urgent. Insulin’s instability also reflects broader challenges in biologics, where many protein based therapeutics degrade easily. Incorporating non canonical building blocks offers a promising strategy to enhance protein stability across medicine and biotechnology.
Description of invention
Researchers introduced a novel non-canonical histidne analogue, having NH‑triazole building block, into specific positions of human insulin, enhancing intramolecular and intermolecular interactions that stabilize the molecule.
Key Advantages
- Thermal stability up to 95 °C
- Retains full biological activity after extreme heat exposure
- Increased resistance to enzymatic degradation
- Higher affinity for metal ions, enabling alternative stabilization and purification pathways
- Simplified production and distribution, potentially eliminating cold‑chain requirements
- This creates a high‑value, next‑generation insulin that could reshape the competitive landscape.
Main advantages
- Significant reduction in storage and transport costs
- Lower spoilage rates = improved margins
- Ability to penetrate untapped high‑population markets
- Competitive differentiation through superior formulation stability
- Potential for premium temperature‑stable insulin products