News
Customize list
-

Planning Renewable Energy Without Conflict?
The transition to renewable energy is a political necessity. But how can it be implemented without compromising other vital objectives – such as biodiversity conservation, water management, cultural heritage preservation, and public health – while also ensuring active public engagement?
-

How nanoparticles for fuel cell applications continuously change
Proton exchange membrane fuel cells use hydrogen as a fuel and are one possible alternative to internal combustion engines that run on fossil fuels. The wider deployment of fuel cells, and thus the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, is hampered by their cost. They require the expensive and scarce metal platinum to operate efficiently.
-

A completely new concept for harnessing waste heat and solar energy
Researchers from the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering at the University of Ljubljana, led by Assistant Professor Dr. Primož Poredoš, in collaboration with researchers from the ITEWA Innovation Team at Shanghai University, have developed a new concept for utilizing ultra-low temperature (waste) heat by simultaneously introducing solar energy and low-temperature heat into the system. They are the first in the world to present an entirely new concept for producing distilled water from saline, untreated water using thermally driven membrane distillation (MD).
-

Improving the Quality of Life in Arid Areas with a System for Generating Electricity and Fresh Water
In parts of the world where water is increasingly scarce, it is crucial to establish effective and sustainable systems for energy and water supply. The interdisciplinary project PV-W2WFresh is changing the way we think about solar energy and water scarcity, aligning with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG 6 and 7) by promoting clean energy and water availability in rural and underserved regions. This cutting-edge research combines concentrated photovoltaic (CPV) technology with an innovative evaporation desalination process, creating a system that not only generates electricity but also provides a continuous source of clean drinking water.
-

Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Successful in MSCA Doctoral Networks Call
The University of Ljubljana, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, has been successful in the Horizon Europe Marie Skłodowska-Curie Actions (MSCA) Doctoral Networks call with the project UPCYCLE – Dissemination of Advanced Conversion Routes for Hard-to-Recycle Biogenic Waste. As part of the project, 15 doctoral candidates will be trained, three of whom will be based in Slovenia. The project is coordinated by Politecnico di Milano, with UL FS participating as a partner.
-

Reorganization of Social Work Centers Between Declared and Actual
How successful was the reorganization of Social Work Centers (SWC), implemented in 2018 by the Ministry of Labor, Family, Social Affairs, and Equal Opportunities? The ministry, SWC employees, and users have different opinions. This was found in the doctoral dissertation "Evaluation of the Reorganization of Social Work Centers in the Republic of Slovenia from the Perspective of Selected Public Governance Models" by Dr. Matej Babšek from the Faculty of Public Administration at the University of Ljubljana. This exceptional work earned him the Mzia Mikeladze award, presented by the Network of Institutes and Schools of Public Administration in Central and Eastern Europe (NISPAcee) for outstanding doctoral dissertations in the field of public administration and public policies.
-

Harnessing the low temperatures of space to cool buildings and equipment in remote locations in an environmentally friendly way
Doc. dr. Professor Primož Poredoš, in collaboration with colleagues from the Laboratory for Environmental Technologies in Buildings at the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, UL, and researchers from the ITEWA innovation team at Shanghai University, has developed a concentrator based on the AsymSkyCool method that enables cooling of buildings and appliances without the use of electricity. The concentrator takes advantage of the 'cold of space' – the extremely low temperatures of deep space, which can be as low as minus 15°C compared to the surrounding environment – and uses a special method to concentrate it and direct it towards a heat source. Using space as a cooling source enables environmentally friendly, efficient and sustainable cooling of devices that consume large amounts of electricity, such as LED lights, batteries and electric motors.
-
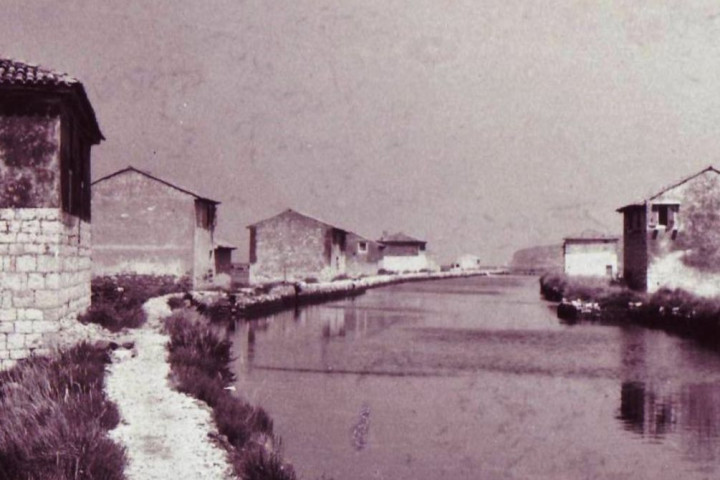

Use of ship technology for self-maintenance of saltpan cottages
Ship technology could offer a solution for the saltpan cottages which are falling inexorably into ruin in the area of the Sečovlje saltpans. This has been determined by students of various University of Ljubljana faculties under the mentorship of Senior Lecturer Mag. Valter Suban of the University’s Faculty of Maritime Studies and Transport. They were aware of the problem of degradation in the area of the Sečovlje saltpans, so they were looking for a way for the saltpan cottages to be reconstructed and changed into sustainable self-maintaining projects.
-
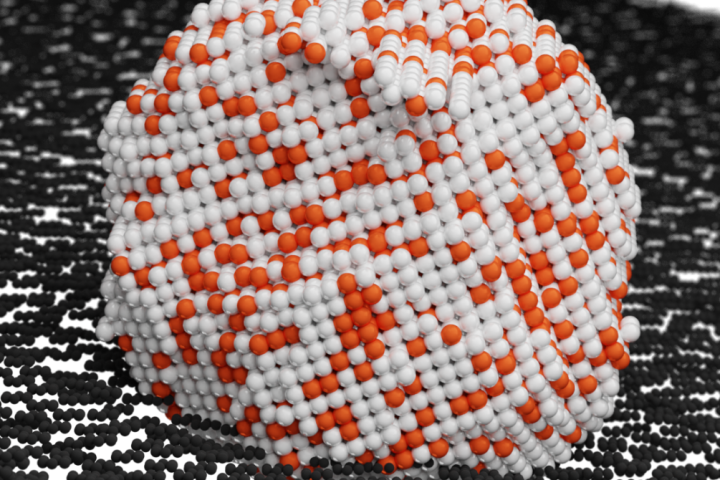
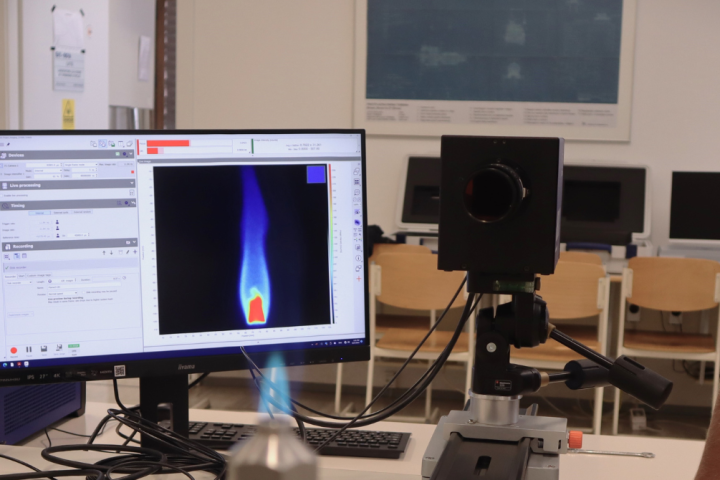
Irregularities in hydrogen fuel cell catalysts
The increasingly evident consequences of climate change are a major motivation for the development of low-carbon technologies, among which fuel cells, using hydrogen as fuel, hold great promise. One of the obstacles to the wider commercialization of the technology is the use of expensive and rare platinum in catalysts, which is why effort goes into trying to reduce the amount of platinum used while preserving the relevant properties of these materials. For the oxygen reduction reaction, one of the reactions in a fuel cell, we use catalysts with alloyed nanoparticles containing platinum and cheaper transition metals. Since certain defects in the nanoparticle structure can occur during the preparation of the catalyst, the effects of all aspects of the structure on the performance in the fuel cell need to be studied in detail.
-
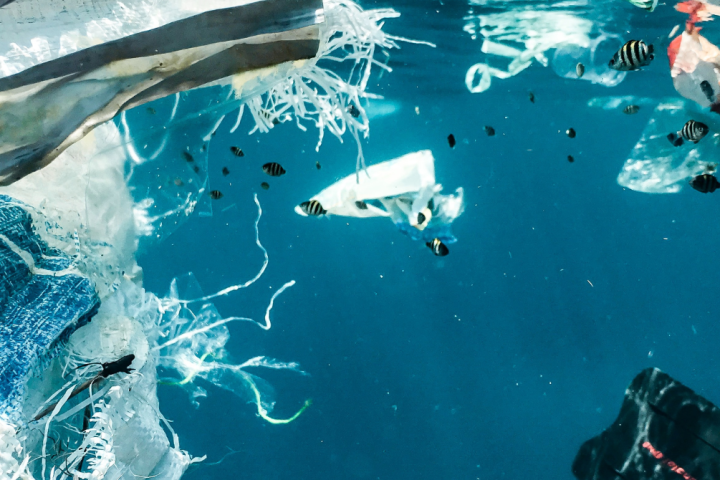

Using cavitation to break down invisible water pollutants
Researchers from the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and the National Institute of Chemistry conducted an experimental study in which they achieved the degradation of a water-soluble synthetic polymer - poly(vinyl alcohol) PVOH - by acoustic and hydrodynamic cavitation. The use of PVOH is rapidly increasing, and as a result, increasing amounts of this material are being released into the environment. PVOH is widely used in the textile and paper industries, as well as in households, for example in the form of detergent pods. It is estimated that thousands of tons of it are washed into the aquatic ecosystem every year.
-
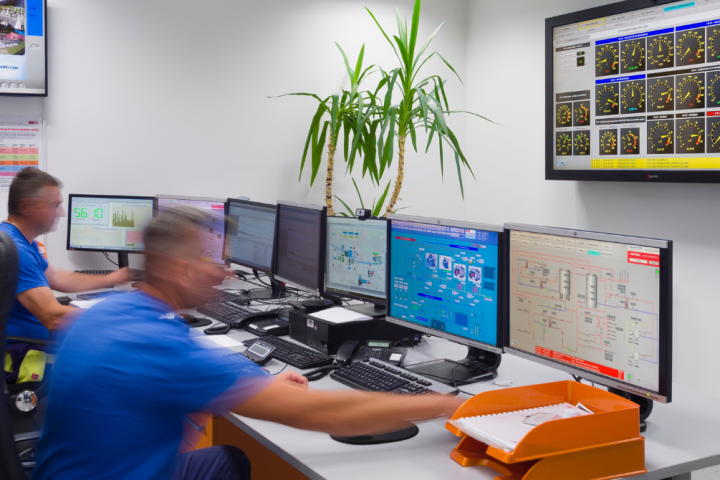

The innovative solutions for the use of flexibility in the power system
The increasing share of renewable distributed energy resources (DERs) in the power system is becoming a key for the decarbonization of the European energy sector and thus achieving the EU's energy and climate change policy objectives. The variability and uncertainty of the DERs generation present significant risks and challenges related to the stability and reliability of the entire interconnected European power system, as well as national and even small local networks while opening new opportunities for the development of new energy concepts and solutions.
-

Biotechnical Faculty and partners free up potential European rural areas for transition to circular bioeconomy
Based at the Biotechnical Faculty of the University of Ljubljana, a new Horizon Europe coordination and support project is underway to develop a working framework for introducing circular small-scale bio-based solutions in rural areas. Assoc. Prof. Dr Luka Juvančič, head of the project at the Biotechnical Faculty in the Chair for Agrarian Economics, Policy Law of the Animal Science Department, explains: “The aim of the BioRural project is to address economic, demographic and climate challenges for the most remote rural communities, through the presentation of circular technological and organisational solutions in various fields of bioeconomy (agricultural and food systems, the forest-wood chain, water systems, bioenergy, biomaterials).” He pointed out that European rural areas should not just succumb to the role of a source of raw materials for the bioeconomy, but should strengthen local value chains that will contribute to increased income and new rural employment.
