News
Customize list
-

Can droplets reveal the pressure threshold of water-repellent surfaces?
Researchers from the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering at the University of Ljubljana developed a simple yet remarkably precise method that can determine, from a single drop of water, when superhydrophobic surfaces lose their water-repellent properties. This breakthrough will aid in the development of more durable water-repellent materials that can be used in industry, for example in cooling, self-cleaning, or corrosion protection.
-

How Micro- and Nanoplastics (MNPs) Are Shaping European Agricultural Soils
Modern agriculture relies heavily on plastic products such as mulch films, greenhouses, and irrigation systems. However, a significant portion of this plastic ends up as micro- and nanoplastics in the soil. How does this affect ecosystems and food production across Europe? This is the central question addressed by the MINAGRIS project.
-

How to Enrich the Nutritional Value of Flour – Collaboration Between Slovenian Industry and Academia
Researchers from the Biotechnical Faculty and the Faculty of Chemistry and Chemical Technology at the University of Ljubljana have successfully developed a process for improving the nutritional value of pea flour through lactic acid fermentation. The interdisciplinary study, conducted in collaboration with a Slovenian food processing company goes beyond academic boundaries and presents a significant commercial value for the techonlogical application on an industrial scale.
-

Dr. Liju Raju is a recipient of the MSCA 2024 Postdoctoral Fellowship at UL FKKT
Dr. Liju Raju, post-doctoral researcher at the University of Ljubljana, has been awarded the prestigious Marie Skłodowska-Curie Action (MSCA) postdoctoral fellowship for his project CHITOCAT. The research work will be conducted at the Faculty of Chemistry and Chemical Technology under the mentorship of Dr. Ross Jansen van Vuuren.
-

Revolution in manufacturing: Machine learning improves the precision of sheet metal stamping
Advancements in sheet metal stamping processes are creating new opportunities in industrial production. Researchers from the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering at the University of Ljubljana have developed an advanced method that uses machine learning to improve accuracy and reduce material waste.
-

Digital Nomads Reveal the Future of Work: What Do Their Stories on Reddit Tell Us?
The way we work has changed significantly in recent years, and in the coming years, it will become even more digital, mobile, and tailored to individuals. Digital nomads play a crucial role in this transformation. What drives them to choose this lifestyle, how do they shape their careers, and in what ways do they build their networks? Answers to these questions are provided by a study, which included Professor Dr. Matej Černe from the School of Economics and Business at the University of Ljubljana, analyzing over 66,000 discussions on the Reddit forum Digital Nomad.
-

Greentech: Hybrid Technologies for Factories of the Future and the Green Transition
A reduction of CO2 emissions by 17 million tons, energy savings of nearly 9 billion kWh, and a decrease in material consumption by approximately 800,000 tons over ten years. These are the expected outcomes of the groundbreaking Greentech program, which brings together 11 partners from academia and industry. The program is led by the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering at the University of Ljubljana.
-
Comprehensive Overview of Plasma Electrolytic Polishing
Additive technologies are increasingly used for the production of metal components as they allow for efficient shape customization in a short time and with reduced material consumption. However, the lower surface quality of printed parts limits their direct industrial use. The growing demand for post-processing of metal parts produced by additive technologies highlights the potential of PeP technology as an environmentally friendly and efficient polishing method.
-

Developing sustainability communication is the key to a better future
Sustainability communication is becoming increasingly important in addressing pressing environmental and social issues. If done effectively, it can contribute to the faster adoption of sustainable practices and the improvement of public awareness. In doing so, it should not only focus on avoiding greenwashing but also on how to effectively engage stakeholders in complex sustainability challenges.
-

Transforming food waste into sustainable soil improvers
Food waste is a major challenge of modern times. How to reduce it and use it usefully? This challenge will be faced by the partners on the Waste4Soil project. The living laboratories will look for new technological solutions and products to reduce the amount of food waste by recycling it into soil improvers and biostimulants.
-

LANDLABS - Landscape Laboratories: Design Strategies for Sustainable and Beautiful Landscapes of the Anthropocene
How can landfills, mining areas or transportation infrastructure corridors that are part of our urban landscape be transformed into sustainable and beautiful places? How can we create a coexistence between humans, animals, plants, water, soil and technical elements in these areas? These are the questions addressed by LANDLABS, a doctoral research project in the field of landscape planning and design, which was successfully funded in April 2024 as part of the call for Marie Sklodowska-Curie Doctoral Networks.
-
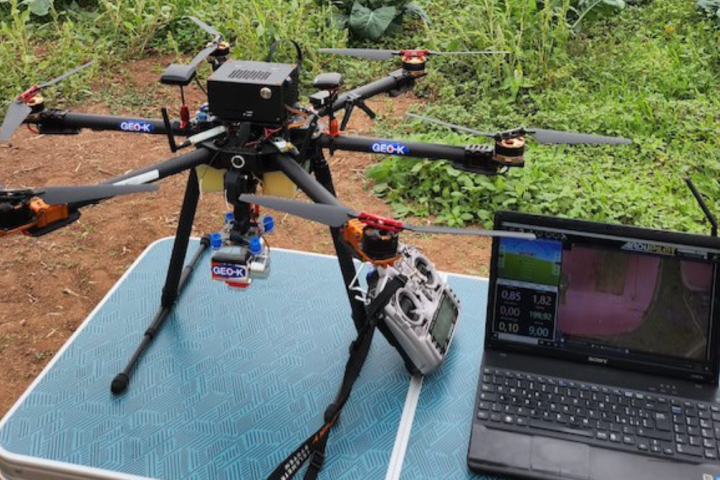

New Technology developed at UL FRI Makes Drone-Based Precision Agriculture More Efficient
Researchers at UL's Faculty of Computer and Information Science (FRI) have made a significant breakthrough in drone-based precision agriculture with a new AI technology. Limited onboard processing power in drones usually leads to the processing of the acquired images to take place post-flight, when they are downloaded and analyzed on a separate computer. Dr. Octavian Machidon's team, working on the H2020 Smart4All AgriAdapt project in 2023, tackled this limitation head-on. They developed an energy-efficient, adaptive framework enabling real-time processing of UAV images onboard the drone itself.
-
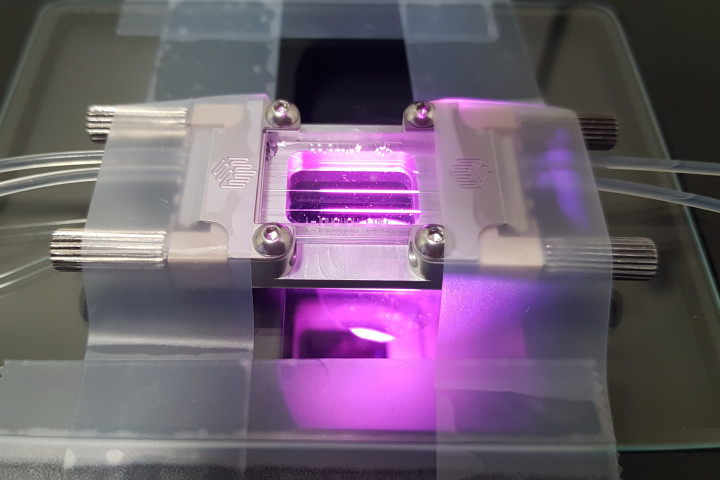
Researchers from the Faculty of Chemistry and Chemical Technology of the University of Ljubljana have obtained a Twinning project in the field of continuous (bio)catalytic processes
Under the leadership of Prof. Dr. Polona Žnidaršič Plazl, researchers from the Faculty of Chemistry and Chemical Technology of the University of Ljubljana (UL FKKT) have obtained a Twinning project titled "Twinning for Building Excellence and Innovative Solutions in Flow Catalysis" – FlowCat.
-

Food for thought: discussing the menu of the future with scientists
The University of Ljubljana invites you to the Food for thought Festival, a series of interdisciplinary events organised by the University in collaboration with the "Jožef Stefan" Institute and the Institute of Chemistry. The festival menu has a sustainable theme and brings together researchers, UL alumni and students around a common table to discuss current societal issues and the challenges of creating sustainable food systems. The events, which will take place between 23 and 25 April, are free of charge,intended for the broader public and (most of them) can also be attended online.
-

Doc. dr. Jaka Tušek from UL FS recieves ERC funding to support his research on elastocaloric technology
Dr. Jaka Tušek, Assistant Professor at the University of Ljubljana’s Faculty of Mechanical Engineering (UL FS), and his research team are developing elastocaloric cooling and heating technology. The ground-breaking research carried out under the ERC Starting Grant (StG) as part of the SUPERCOOL project has been rewarded with a successful application for an ERC Proof-of-Concept (PoC) Grant with the E-CO-HEAT project, providing support for the innovation potential of research achievements. This makes Tušek the sixth ERC researcher in Slovenia, and the second at UL FS, to receive additional support to develop the innovative potential of his research. The E-CO-HEAT project will be based on the elastocaloric device developed in the SUPERCOOL project, which was the first in the world to demonstrate sustained dynamic performance and record-breaking cooling and heating characteristics, and whose specific characteristics exceed all caloric cooling devices built to date. The ERC PoC funding will enable the technology to be further developed and, together with the relevant business strategy and intellectual property, to be transferred into everyday use.
-
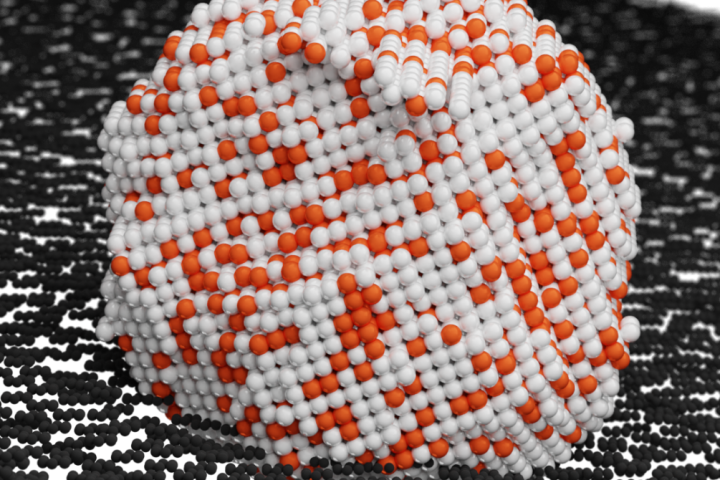
Irregularities in hydrogen fuel cell catalysts
The increasingly evident consequences of climate change are a major motivation for the development of low-carbon technologies, among which fuel cells, using hydrogen as fuel, hold great promise. One of the obstacles to the wider commercialization of the technology is the use of expensive and rare platinum in catalysts, which is why effort goes into trying to reduce the amount of platinum used while preserving the relevant properties of these materials. For the oxygen reduction reaction, one of the reactions in a fuel cell, we use catalysts with alloyed nanoparticles containing platinum and cheaper transition metals. Since certain defects in the nanoparticle structure can occur during the preparation of the catalyst, the effects of all aspects of the structure on the performance in the fuel cell need to be studied in detail.
-
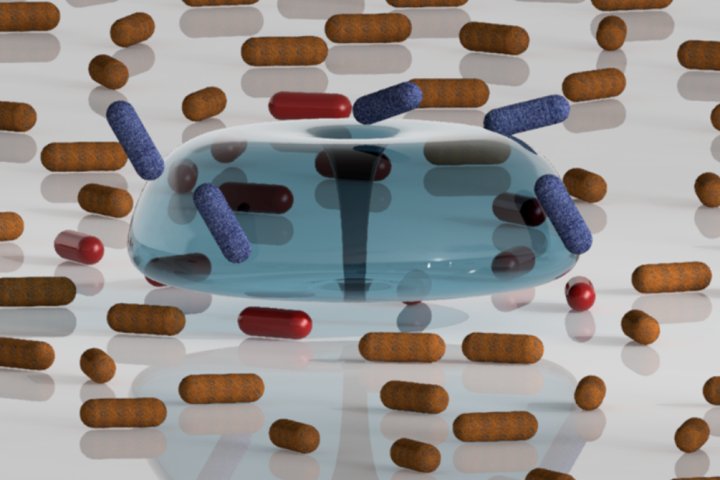

Treating wastewater through cavitation and understanding the effects of bubbles on bacterial cells
Increasing environmental pollution and drinking water shortages are a growing socioeconomic problem, in which cavitation technology can contribute to a cleaner and greener approach to wastewater treatment. Cavitation is a physical phenomenon that describes the phase change from liquid to vapour and back at constant temperature. The mechanical, thermal and chemical effects of cavitation can be utilised for various purposes, including to inactivate microorganisms in drinking water and wastewater. It has been proven that cells are subjected to damage in the immediate vicinity of a bubble. Further numerical analysis has identified the formation of microjets as a possible mechanism of bacterial cell damage.
-
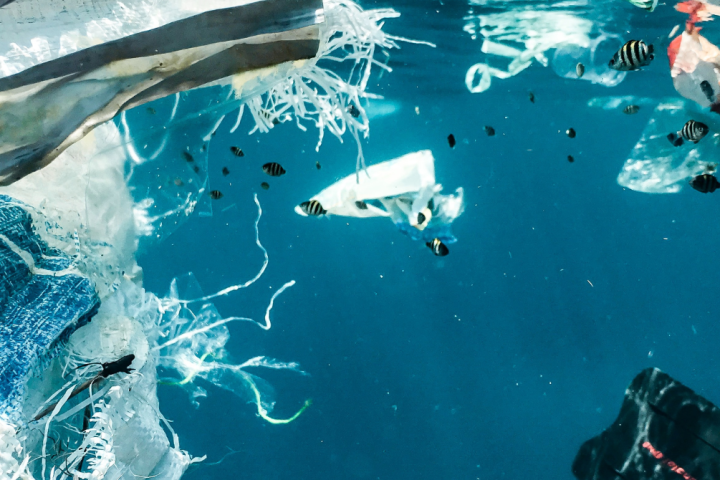

Using cavitation to break down invisible water pollutants
Researchers from the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and the National Institute of Chemistry conducted an experimental study in which they achieved the degradation of a water-soluble synthetic polymer - poly(vinyl alcohol) PVOH - by acoustic and hydrodynamic cavitation. The use of PVOH is rapidly increasing, and as a result, increasing amounts of this material are being released into the environment. PVOH is widely used in the textile and paper industries, as well as in households, for example in the form of detergent pods. It is estimated that thousands of tons of it are washed into the aquatic ecosystem every year.
-

The innovative solutions for the use of flexibility in the power system
The increasing share of renewable distributed energy resources (DERs) in the power system is becoming a key for the decarbonization of the European energy sector and thus achieving the EU's energy and climate change policy objectives. The variability and uncertainty of the DERs generation present significant risks and challenges related to the stability and reliability of the entire interconnected European power system, as well as national and even small local networks while opening new opportunities for the development of new energy concepts and solutions.
-

Biotechnical Faculty and partners free up potential European rural areas for transition to circular bioeconomy
Based at the Biotechnical Faculty of the University of Ljubljana, a new Horizon Europe coordination and support project is underway to develop a working framework for introducing circular small-scale bio-based solutions in rural areas. Assoc. Prof. Dr Luka Juvančič, head of the project at the Biotechnical Faculty in the Chair for Agrarian Economics, Policy Law of the Animal Science Department, explains: “The aim of the BioRural project is to address economic, demographic and climate challenges for the most remote rural communities, through the presentation of circular technological and organisational solutions in various fields of bioeconomy (agricultural and food systems, the forest-wood chain, water systems, bioenergy, biomaterials).” He pointed out that European rural areas should not just succumb to the role of a source of raw materials for the bioeconomy, but should strengthen local value chains that will contribute to increased income and new rural employment.
